营养研究室发现钙摄入对体重的作用受年龄、性别以及BMI等因素的影响
2016-12-29 11:15:22
Li P, Fan C, Lu Y, Qi K*. Effects of Calcium Supplementation on the Body Weight: A Meta-Analysis. Am J Clin Nutr.2016; 104(5):1263-1273(SCI, IF 6.703)
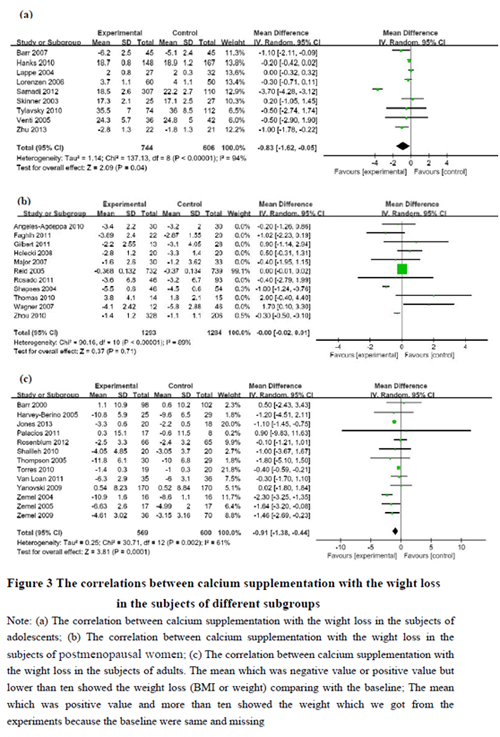
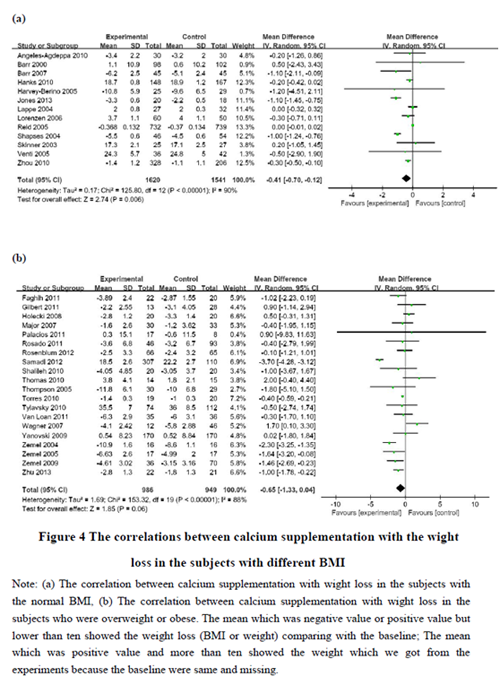
Abstract Background: Whether calcium supplementation reduces body weight and prevents obesity remains unclear because of inconsistent reports. Objective: This meta-analysis was performed to investigate the correlations between calcium intake and changes in body weight based on subjects’ age, gender and BMI and length of calcium intervention. Design: The PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Knowledge and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) databases were systematically searched to select relevant studies published from 1994 to 2016. Both randomized controlled trials and longitudinal studies of calcium supplementation were included, and a random effects model in RevMan 5.3 software was used for data analysis. Results: Thirty-three studies involving a total of 4,733 participants were included in this meta-analysis. No significant differences in weight loss were found between the calcium intervention and the control groups (-0.01, 95%CI -0.02, 0.00 kg) (P=0.12). However, negative correlations between calcium supplementation and weight changes were shown in children and adolescents (-0.26, 95%CI -0.41, -0.11 kg) (P<0.001) and adult men and premenopausal women (-0.91, 95%CI -1.38, -0.44 kg) (P<0.001), but not in postmenopausal women (-0.14, 95%CI -0.54, 0.26 kg) (P=0.50). Considering BMI, a negative correlation between calcium supplementation and weight changes were observed in subjects with a normal BMI (-0.53, 95%CI -0.89, -0.16 kg) (P=0.005) but not in overweight or obese subjects (-0.35, 95%CI -0.81, 0.11 kg) (P=0.14). Compared to the control groups, no differences in weight change were shown in the calcium intervention groups when the calcium intervention was shorted (-0.09, 95%CI -0.45, 0.26 kg) (P=0.60) or longer than 6 months (-0.01, 95%CI -0.02, 0.01 kg) (P=0.46). Conclusions: Increasing calcium intake through calcium supplements could reduce body weight in subjects who have a normal BMI or in children, adolescents, adult men and premenopausal women.
本研究通过PubMed、Embase及中国知网(CNKI)等数据库共纳入了1994到2016年出版的33篇有关钙补充与肥胖的相关研究,利用RevMan 5.3软件的随机效应及固定效应模型进行Meta分析,结果发现整体钙干预组和对照组相比,体重无显著性差异。而后根据研究对象的年龄、性别、体重指数和钙干预的长度进行分层,并对钙摄入量进行了限定,以便控制相关混杂因素后进行相关性的探讨,结果显示通过钙补充剂增加钙的摄入量可以减少BMI正常人、儿童和青少年、成年男性及绝经前妇女的体重,而对于肥胖患者和绝经期妇女的体重无影响,提示保证适量的钙摄入有助于肥胖的预防,但对于已经发生肥胖的干预治疗无明显效果。
上一篇: 耳鼻咽喉头颈外科研究室研究发现MicroRNA hsa-miR-25-3p可抑制人肝细胞中CYP2B6的表达和药物诱导




